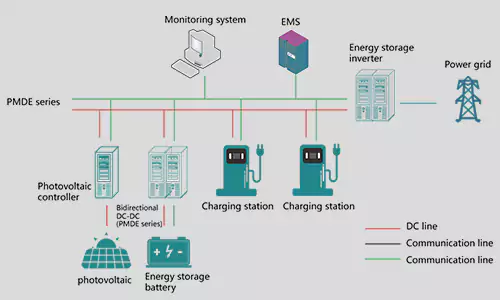
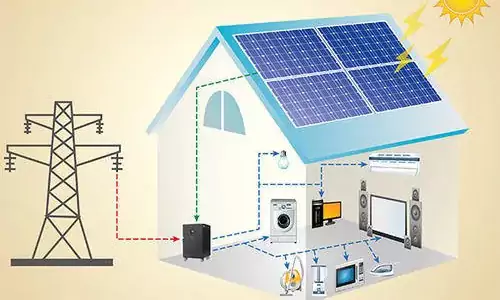
In electrical power systems, DC bus and AC bus are critical components that facilitate the distribution of power within a network. Below is an explanation of their concepts and wiring schemes:
1. DC Bus (Direct Current Bus)
- Definition: A DC bus is a common connection point for distributing direct current (DC) power within a system. It acts as a central hub where multiple DC sources, loads, and energy storage devices are connected.
- Applications: Commonly used in solar power systems, battery storage systems, electric vehicles, and data centers.
- Components Connected:
- Solar panels (via charge controllers).
- Batteries (for energy storage).
- DC loads (e.g., LED lighting, DC appliances).
- Inverters (to convert DC to AC for AC loads).
- Wiring Scheme:
- All DC sources and loads are connected in parallel to the DC bus.
- Proper fuses or circuit breakers are installed to protect against overcurrent.
- A charge controller or DC-DC converter may be used to regulate voltage levels.
- Advantages:
- Efficient for systems with multiple DC sources and loads.
- Simplifies wiring and reduces energy losses in DC systems.

2. AC Bus (Alternating Current Bus)
- Definition: An AC bus is a common connection point for distributing alternating current (AC) power within a system. It serves as a central hub for AC sources, loads, and grid connections.
- Applications: Widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial power systems, as well as in hybrid renewable energy systems.
- Components Connected:
- Grid connection (for grid-tied systems).
- Inverters (to convert DC from solar panels or batteries to AC).
- AC generators (e.g., diesel or gas generators).
- AC loads (e.g., household appliances, machinery).
- Wiring Scheme:
- All AC sources and loads are connected in parallel to the AC bus.
- Circuit breakers and protective devices are installed to ensure safety and reliability.
- A transfer switch may be used to switch between grid power and backup power sources (e.g., generators or inverters).
- Advantages:
- Compatible with standard AC appliances and grid infrastructure.
- Enables seamless integration of renewable energy sources with the grid.

Key Differences Between DC Bus and AC Bus:
| Aspect | DC Bus | AC Bus |
|---|---|---|
| Current Type | Direct Current (DC) | Alternating Current (AC) |
| Voltage Level | Typically lower voltage (e.g., 12V, 24V, 48V) | Higher voltage (e.g., 120V, 230V, 400V) |
| Applications | Solar systems, batteries, EVs | Grid-tied systems, household/commercial power |
| Wiring Complexity | Simpler for DC-only systems | More complex due to phase and frequency considerations |
| Efficiency | High efficiency for DC loads | Slightly lower due to AC-DC conversion losses |
Combined DC and AC Bus Systems:
In hybrid renewable energy systems, both DC and AC buses are often used together:
- DC Bus: Connects solar panels, batteries, and DC loads.
- AC Bus: Connects the inverter, grid, and AC loads.
- Integration: A bi-directional inverter or hybrid inverter manages power flow between the DC and AC buses, ensuring optimal energy utilization.
Example Wiring Diagram:
- DC Side:
- Solar panels → Charge controller → DC bus → Batteries and DC loads.
- AC Side:
- Inverter → AC bus → Grid connection and AC loads.
- Control:
- Energy management system (EMS) monitors and optimizes power flow between DC and AC buses.
Conclusion:
DC and AC bus wiring schemes are fundamental to modern power systems, enabling efficient distribution and management of electricity. While DC buses are ideal for systems with DC sources and loads, AC buses are essential for integrating with the grid and powering standard AC appliances. In hybrid systems, combining both buses allows for flexible and reliable energy management.