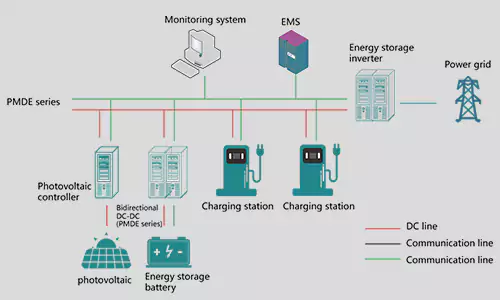
Electric vehicle (EV) charging stations, also known as EV chargers or EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment), come in several types, each with different power levels, charging speeds, and use cases. Below are the main types of EV charging stations and their key differences:
1. Level 1 Charging (AC Charging)
- Power Supply: 120V AC (standard household outlet).
- Charging Speed: 3-5 miles of range per hour (very slow).
- Use Case:
- Suitable for overnight charging at home.
- Ideal for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) or EVs with small batteries.
- Advantages:
- No special installation required; uses existing outlets.
- Low cost.
- Disadvantages:
- Extremely slow charging speed.
- Not practical for long-distance travel or daily use of high-capacity EVs.
2. Level 2 Charging (AC Charging)
- Power Supply: 240V AC (similar to large home appliances like dryers).
- Charging Speed: 12-60 miles of range per hour (moderate speed).
- Use Case:
- Common for home, workplace, and public charging stations.
- Suitable for daily charging of most EVs.
- Advantages:
- Faster than Level 1, making it practical for most EV owners.
- Widely available in public locations (e.g., shopping centers, parking lots).
- Disadvantages:
- Requires professional installation of a dedicated 240V circuit.
- Higher upfront cost compared to Level 1.
3. Level 3 Charging (DC Fast Charging)
- Power Supply: 400V-900V DC (high-power direct current).
- Charging Speed: 60-100 miles of range in 20-30 minutes (very fast).
- Use Case:
- Designed for long-distance travel and quick top-ups.
- Commonly found along highways, in commercial areas, and at dedicated charging stations.
- Advantages:
- Extremely fast charging, ideal for road trips.
- Reduces downtime for EV drivers.
- Disadvantages:
- Expensive to install and operate.
- Not all EVs support DC fast charging (check compatibility).
- Frequent use may impact battery longevity.
4. Tesla Supercharger (Proprietary DC Fast Charging)
- Power Supply: 480V DC (Tesla-specific).
- Charging Speed: Up to 200 miles of range in 15-20 minutes (ultra-fast).
- Use Case:
- Exclusive to Tesla vehicles.
- Designed for long-distance travel and rapid charging.
- Advantages:
- Fastest charging option for Tesla owners.
- Extensive network of Supercharger stations globally.
- Disadvantages:
- Only compatible with Tesla vehicles.
- Higher cost compared to standard Level 2 charging.
5. Wireless Charging (Inductive Charging)
- Power Supply: Varies (typically Level 2 equivalent).
- Charging Speed: Similar to Level 2 charging (moderate speed).
- Use Case:
- Emerging technology for home and public use.
- Eliminates the need for physical cables.
- Advantages:
- Convenient and user-friendly.
- Reduces wear and tear on charging ports.
- Disadvantages:
- Slower than Level 3 charging.
- Higher installation and equipment costs.
- Limited availability and compatibility.
Key Differences Between Charging Types:
| Feature | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 (DC Fast) | Tesla Supercharger | Wireless |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power Supply | 120V AC | 240V AC | 400V-900V DC | 480V DC | Varies (typically 240V AC) |
| Charging Speed | 3-5 miles/hour | 12-60 miles/hour | 60-100 miles/20-30 mins | Up to 200 miles/15-20 mins | Similar to Level 2 |
| Installation Cost | Low | Moderate | High | High | High |
| Use Case | Overnight home charging | Home, workplace, public | Long-distance travel | Tesla long-distance travel | Convenient home/public use |
| Compatibility | All EVs | All EVs | Most modern EVs | Tesla vehicles only | Limited EV models |
Conclusion:
EV charging stations vary significantly in terms of power, speed, and application. Level 1 is the simplest but slowest, while Level 2 is the most common for daily use. Level 3 (DC Fast Charging) and Tesla Superchargers offer rapid charging for long-distance travel, and wireless charging provides a cable-free alternative. The choice of charging station depends on the EV owner’s needs, vehicle compatibility, and budget.