Magnetic Latching Relay
A magnetic latching relay is a type of electromagnetic relay that uses the interaction between permanent magnets and electromagnets to maintain contact states (open/closed) without continuous power. Key features include:
1. Magnetic Latching Relay Working Principle
- Magnetic Latching Mechanism: Permanent magnets create a stable magnetic field to hold contacts in position. A brief pulse (forward or reverse voltage) to the coil generates an opposing magnetic field, switching the contacts. The state persists after the pulse ends.
- Operation:
- Set: Forward pulse aligns electromagnet and permanent magnet fields, closing contacts.
- Reset: Reverse pulse disrupts alignment, opening contacts.
2. Magnetic Latching Relay Key Features
- Low Power Consumption: Only requires pulse power for switching (no continuous energy use).
- High Stability: No mechanical wear, long lifespan (electrical: ~10k cycles; mechanical: up to millions).
- High Load Capacity: Handles up to 150A current with contact voltage drop <100mV.
3. Differences from Standard Relays
- State Retention: Maintains contact position without power (standard relays require constant power).
- Structure: Incorporates permanent magnets for latching, enhancing reliability.
4. Applications
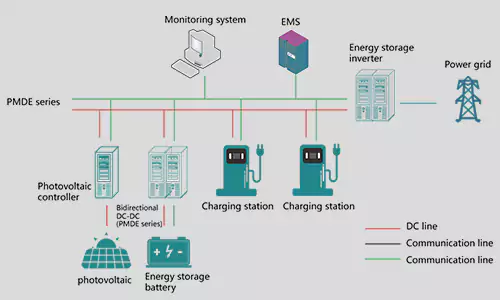
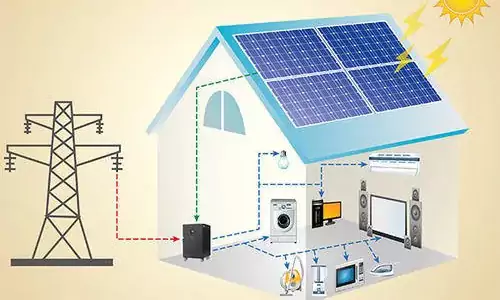
- Smart Meters: Prepaid/three-phase meters (remote power control via low-energy pulses).
- Power Systems: Circuit breaker control, reactive compensation devices.
- Industrial Automation: Production line switching, smart home systems.
- Telecom: Signal routing, interface circuits.
5. Future Trends
- Smart Integration: IoT/AI compatibility for adaptive control.
- Eco-Friendly Design: Material/process optimization for reduced energy and costs.
Summary: Magnetic latching relays excel in energy efficiency, reliability, and high-load scenarios, making them vital for smart grids and automated systems.