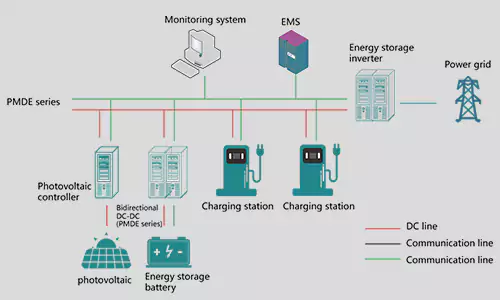
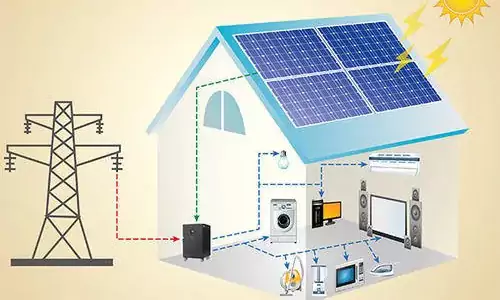
A complete home solar energy storage system consists of several key components that work together to generate, store, and distribute electricity. Below is a breakdown of the essential devices and their roles:
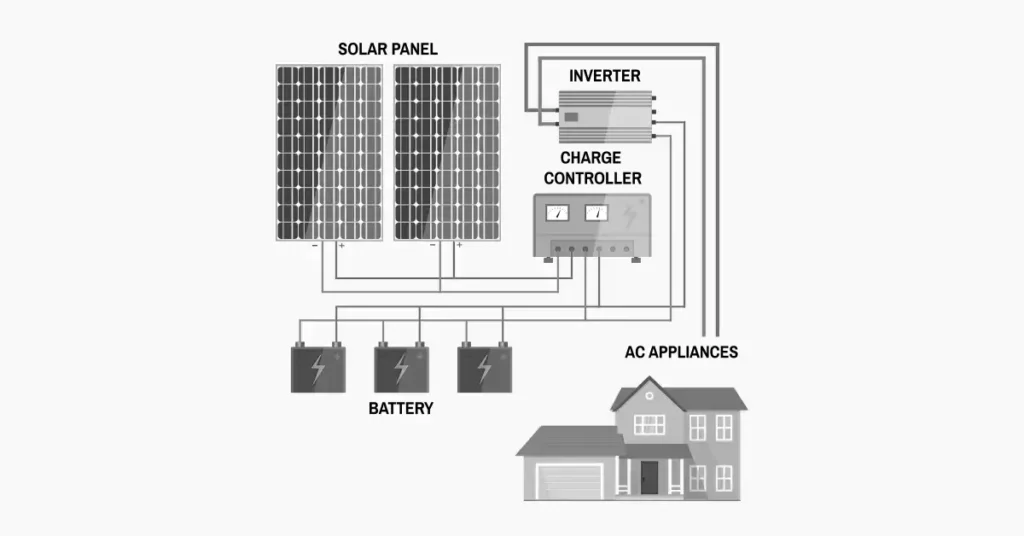
1. Solar Panels (Photovoltaic Modules)
- Function: Convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Details: Made of photovoltaic cells, panels are installed on rooftops or open spaces to maximize sunlight exposure. Their efficiency depends on factors like panel type (monocrystalline, polycrystalline, or thin-film) and environmental conditions.
2. Solar Inverter
- Function: Convert DC electricity from solar panels or batteries into alternating current (AC) for household use.
- Types:
- String Inverter: Connects multiple panels in series (common for grid-tied systems).
- Microinverter: Attached to individual panels for optimized performance (ideal for shaded areas).
- Hybrid Inverter: Manages both solar power and battery storage, enabling grid independence.
3. Battery Storage System
- Function: Store excess solar energy for use during nighttime, cloudy days, or power outages.
- Types:
- Lithium-ion Batteries (e.g., Tesla Powerwall, LG Chem): High efficiency, long lifespan, and compact size.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Lower cost but shorter lifespan and bulkier.
- Key Metrics: Capacity (kWh), depth of discharge (DoD), and cycle life.
4. Charge Controller
- Function: Regulate the voltage and current from solar panels to prevent overcharging or damaging batteries.
- Types:
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Budget-friendly for small systems.
- MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking): More efficient, adjusts to extract maximum power from panels.
5. Energy Management System (EMS)
- Function: Monitor and optimize energy flow between solar panels, batteries, and household loads.
- Features:
- Prioritizes solar energy usage for appliances.
- Manages grid interaction (for hybrid systems).
- Provides real-time data via mobile apps or dashboards.
6. Electrical Panel (Breaker Box)
- Function: Distribute electricity from the solar system, batteries, or grid to household circuits.
- Integration: May include a transfer switch to safely disconnect from the grid during outages (for off-grid or backup systems).
7. Backup Generator (Optional)
- Function: Provide supplemental power during extended periods of low sunlight or high energy demand.
- Common Types: Diesel, propane, or natural gas generators (used in hybrid systems).
8. Mounting and Wiring
- Mounting Racks: Secure panels to rooftops or ground mounts at optimal angles.
- Cabling: High-quality DC and AC wiring to minimize energy loss and ensure safety.
- Safety Devices: Fuses, circuit breakers, and surge protectors to protect against electrical faults.
9. Monitoring System
- Function: Track system performance, energy production, battery status, and consumption patterns.
- Tools: Hardware sensors paired with software (e.g., SolarEdge, Enphase) for remote access and alerts.
System Workflow:
- Solar panels generate DC electricity.
- Charge controller regulates power to batteries (if storage is used).
- Inverter converts DC to AC for household use.
- Excess energy charges batteries or is fed back to the grid (if grid-tied).
- Energy management systems prioritize power sources based on availability and demand.
Key Benefits of a Solar Storage System:
- Energy Independence: Reduce reliance on the grid.
- Cost Savings: Lower electricity bills and avoid peak-rate charges.
- Sustainability: Decrease carbon footprint with renewable energy.
- Resilience: Backup power during outages.
By integrating these components, a home solar storage system provides efficient, reliable, and sustainable energy for daily needs.